Setting Up AWS DMS
What is AWS DMS?:
AWS Data Migration Service (DMS) is a service that allows us to migrate data between a source (in our case, on-premises database) and a target (in our case, Postgres database hosted in AWS).
DMS supported replication types:
-
Continuous replication (CDC):
- When we want to do a one-off migration of all data and then continuously capture new inserts, updates and deletes and reflect them in our target database.
-
One-off data migration:
- When the goal is to migrate all data from a source, and is expected that changes will not be captured and reflected.
Which AWS DMS set up to use?:
For continuous migration:
CDC:
CDC is a SQL server feature, available only on Enterprise and Developer editions.
It allows for changes to be captured (inserts/updates/deletes).
Use case:
When the source database does not have primary keys and you want to migrate data continuously.
MS Replication:
MS Replication is a SQL server feature available on all editions.
It creates a “distribution” database and every time there is a change, it is captured and stored in the “distribution” database.
.MS will then read from that database to reflect the changes in the target database.
Note: The sql user created must have sysadmin permissions to set up replication.
Additional notes: Configuration on the source database is required (please see below section). Additionally, SQL servers DO NOT come with MS replication features pre-installed, so the server might require a set up.
Use cases:
-
When you want to migrate data continuously;
-
When the SQL server is not Enterprise/Developer edition;
-
When the source database has tables, which make use of primary keys;
For one-off set up:
-
No database configuration is required;
-
The sql user must have at least db_owner permissions;
-
The replication runs ones and migrates the data specified;
-
There are no subsequent runs of the migration task, unless triggered with other means;
Use cases:
-
When only a one-off migration is required;
-
When the underlying source database is a reporting server and there are no possible ways to capture updates. In this scenario, we need to daily run a one-off migration, after the reporting server was updated with the latest data;
How to set up DMS:
Database set up:
AWS DMS set up via Terraform:
Both DMS and Postgres can be created via Terraform.
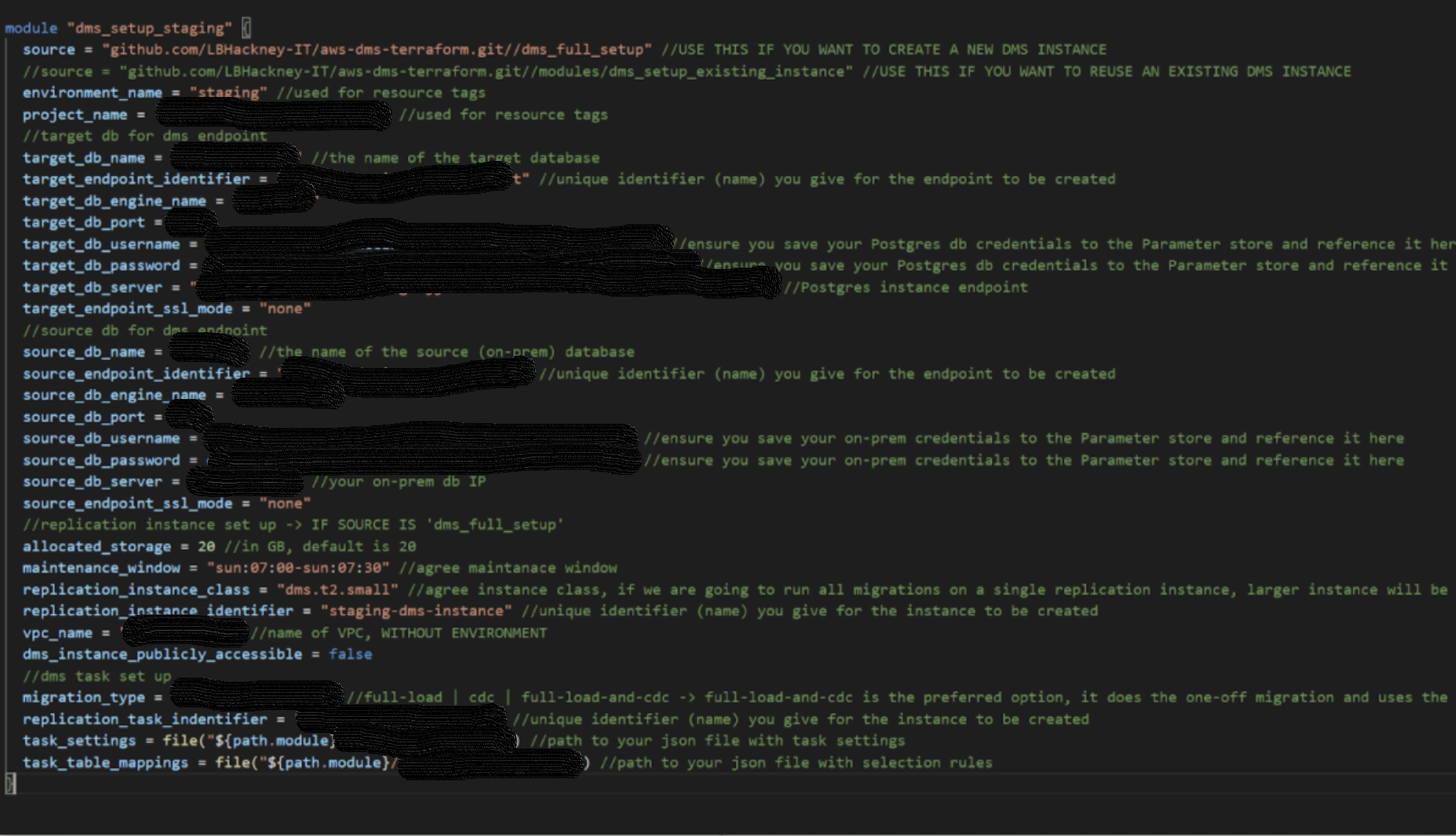
DMS:
Template repository and example usage.
 .
.
Notes::
-
Follow the example usage, which also demonstrates how to add table mappings (specifying which tables are to be replicated);
-
The source DB server should be specified with IP and not the server name;
-
DMS instance should be in the VPC, where the VPN is set up to ensure communication to on-prem is possible;
-
Make sure your DMS instance’s subnet group has only private subnets in it! ;
Postgres:
Template repository and example usage
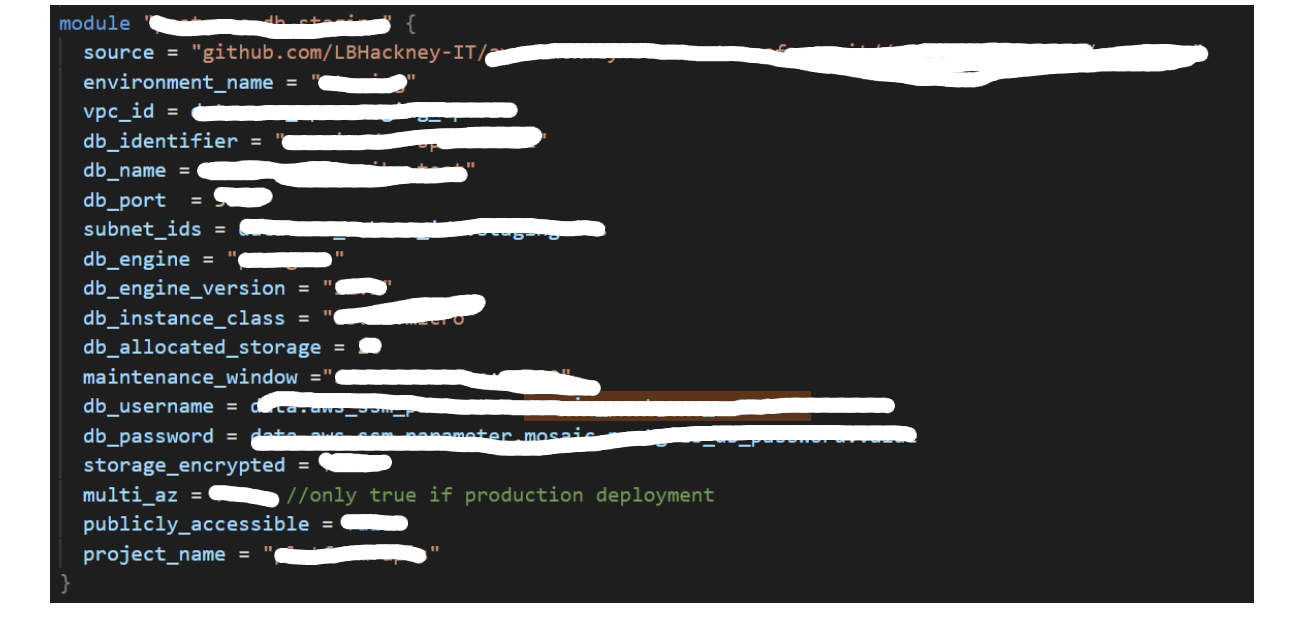
Notes::
- DMS does not support Postgres version 12, so use version 11 or older;
- Always store passwords in parameter store and do not hardcode them;
- “Multi_az” should be true for production databases;
- “subnet_ids” requires subnets in 2 different AZs. Make sure those are private subnets to ensure that the database is secure;
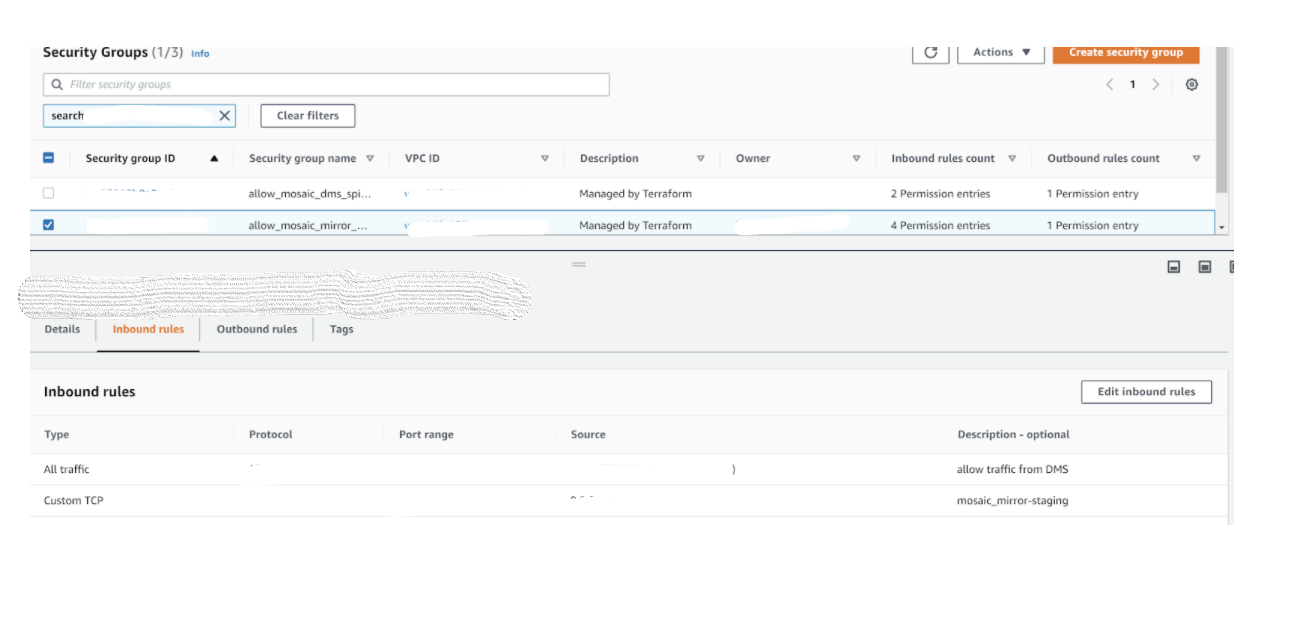
- Currently not terraformed: To enable traffic from DMS to your Postgres instance, ensure you add to the ingress rules of the database’s security group all traffic from DMS security group;
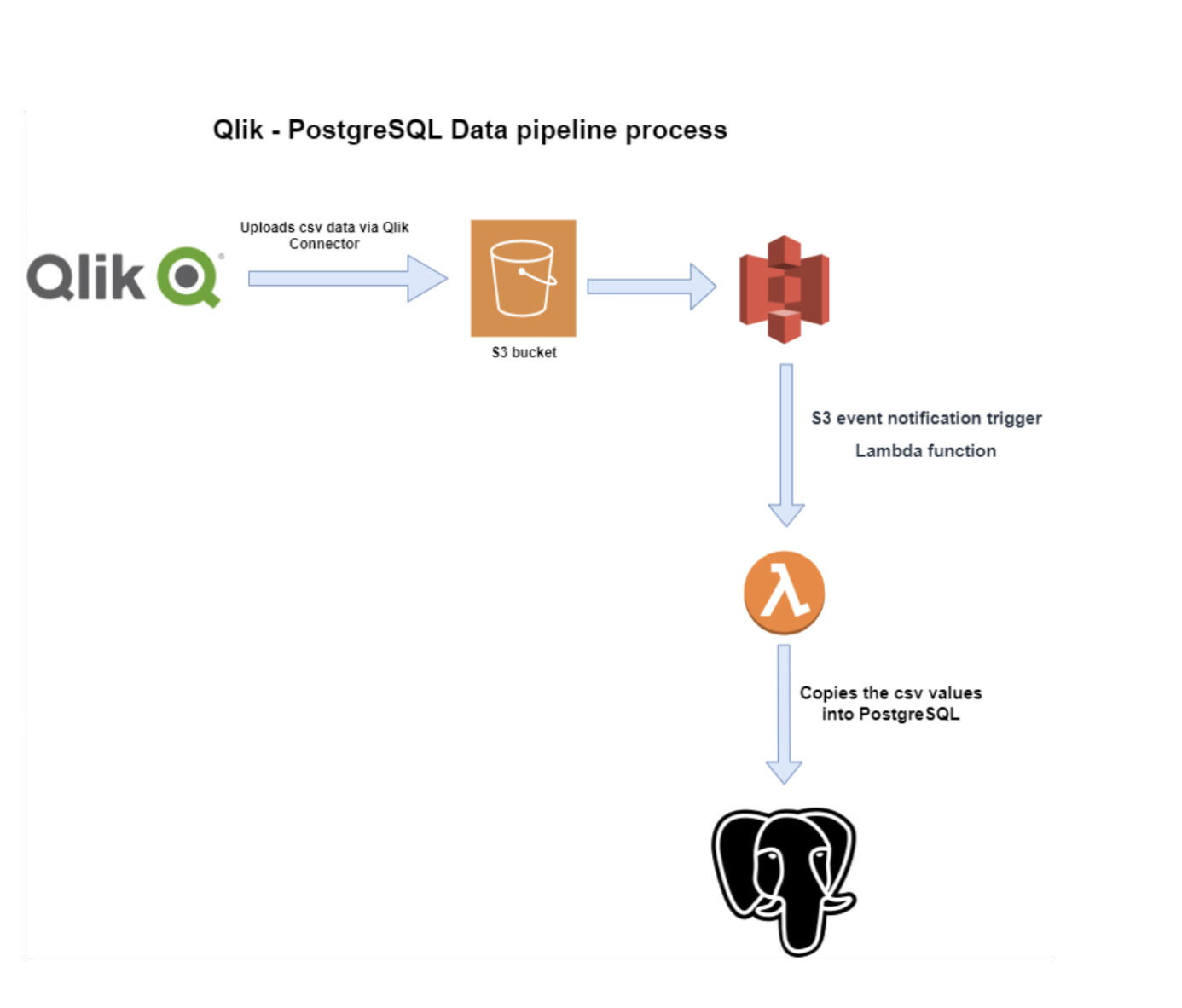
Data migration using a data pipeline:
** What is a data pipeline? **
A data pipeline is an automated flow that gets data stored in one location (source) and uploads it to a target destination.
Data pipeline - CSV to Postgres:
As of 26/06/2020, we have implemented one data pipeline.
The pipeline takes data uploaded in an S3 bucket in .csv format and uploads the data into a Postgres database.